
🎓 Definition
Assortment distribution is deciding which items are sold in which store. This may sound straightforward, but finding the best distribution very often represents the low-hanging fruits of sales growth.
Common Challenges: Retailers’ Teams are often lost in mapping the distribution because of the complexity of:
- Different Range Structures: Which products should be offered?
- Store Formats: Which layout or type of store should be used?
- Store Clustering: Grouping stores based on similar characteristics (store size, location, customer demographics, etc...).
The priority, for both Retailers and Suppliers, is to ensure that items that are both among the Top 20% of national sales and with less than 100% distribution be immediately distributed in all stores.
🧪 Example of Assortment Distribution
Let's consider a supermarket chain named "FreshMart" that operates 100 stores across the country.
FreshMart analyzes national sales data and finds out that "Organic Blueberry Jam" is among the Top 20% of products sold across all stores in the country.
Upon internal checking, FreshMart discovers that "Organic Blueberry Jam" is only available in 60 out of their 100 stores.
FreshMart decided that irrespective of the format or cluster, the "Organic Blueberry Jam" needs to be present in all stores given its national sales performance. They immediately start distributing it to the 40 stores that don't have it.
📅 Frequency
Reviewing items that generate top 20% of national sales every month or at a frequency that suits your market is a common practice. As the market changes, and what's in the top 20% might change as well.
❓Benefits for Optimizing Assortment Distribution
For Retailers:
- Increased Sales: Retailers can capitalize on the popularity of products in the top 20% of national sales. By ensuring they're available across all stores, they can significantly increase sales.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Customers expect to find popular products in stores. By optimizing assortment distribution, Retailers meet customer expectations, leading to higher satisfaction and loyalty.
- Efficient Inventory Management: Retailers can prioritize stocking items with proven sales records, reducing the risk of overstocking less popular items.
- Better Informed Decision Making: Regularly reviewing the assortment distribution provides insights into changing market trends, allowing Retailers to adapt quickly.
For Manufacturers:
- Increased Production Efficiency: Manufacturers can adjust production lines based on the demand from Retailers, ensuring they produce more of what's popular and less of slow-moving products.
- Effective Marketing and Promotions: Knowing which products are in the top 20% of sales allows Manufacturers to channel their marketing efforts effectively, promoting products that have a proven sales record.
- Improved Forecasting: With regular reviews and understanding of the market changes, Manufacturers can anticipate demand shifts and adjust their production and supply chain strategies accordingly.
How do Retailers and Suppliers typically collaborate to optimize assortment distribution?
Retailers and Suppliers often collaborate closely to optimize assortment distribution. One common approach involves sharing sales data and inventory levels to identify which products are performing well and where they should be stocked. Suppliers can provide insights into production capabilities and lead times, allowing retailers to make informed decisions about distribution. Additionally, joint planning sessions and regular communication between Retailers and Suppliers can help align strategies and ensure that both parties are working towards common goals. Collaborative tools and platforms may also be employed to facilitate this partnership, enabling real-time data sharing and collaborative decision-making.
What tools or technologies can be used to streamline the assortment distribution process?
There are several tools and technologies available to streamline the assortment distribution process. Retailers and Suppliers can leverage advanced data analytics software to analyze sales data, forecast demand, and identify trends. Inventory management systems can help optimize stock levels and automate replenishment processes, ensuring that popular products are consistently available across all stores. Additionally, collaborative platforms and supply chain management software can facilitate communication and coordination between Retailers and Suppliers, enabling more efficient and effective assortment distribution. Implementing these technologies can greatly enhance the accuracy, speed, and overall success of assortment distribution strategies.
How can smaller retailers or manufacturers with limited resources implement assortment distribution strategies effectively?
Smaller retailers or manufacturers with limited resources can still implement assortment distribution strategies effectively by focusing on key principles and leveraging available tools and resources. It's essential to prioritize products based on sales performance and customer demand, even if data is limited. Collaborating closely with Suppliers and leveraging their expertise can also be beneficial in making informed decisions about product selection and distribution. Implementing basic inventory management practices, such as regular stock checks and timely replenishment, can help optimize assortment distribution without requiring advanced technologies. Additionally, staying informed about market trends and customer preferences through research and customer feedback can guide smaller retailers and manufacturers in adapting and refining their assortment distribution strategies over time.
🖥️ Make it happen in Ariane
How to access Assortment Distribution in Ariane
Step 1: Select the Pareto Menu in the Range Menu Bar.
Step 2: Select Option in the Filter Menu and choose the KPI, hierarchy level and Promotion filter you want to measure.
Step 3: Select the period you want to measure.
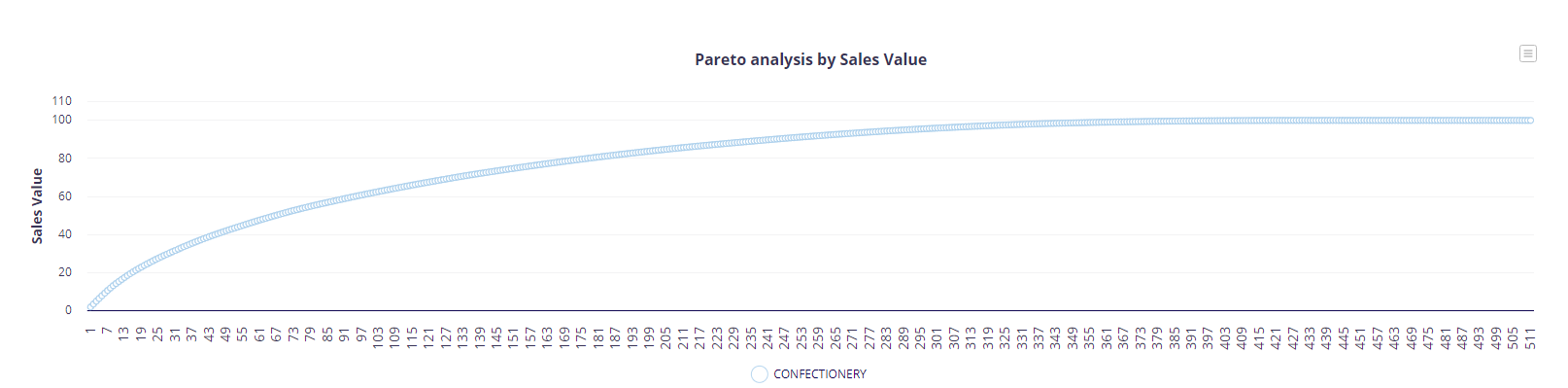
And here it is.


• Range Structures
• Store Clustering
• Assortment Effectiveness