
🎓 Definition
The Category Management Process is the process by which the Retailer (and Manufacturers as well for their own category) assess the performances of its Category and define the required tactics to achieve its financial objectives.
The Retailer Category Management Process ends up with category activity planning and strategic choices for its Suppliers.
When undertaking any Category Management Process, it is important to begin by considering the ultimate objective: What decisions Retailers want to make at the end.
💡What are the Steps in Category Management Process

Seven Steps for Category Management Process
- Category Definition – Determine the products that fit the Category.
- Category Role – Review the purpose of the Category.
- Category Assessment – Assess the Category performance.
- Category Scorecard – Benchmark the Category performance with the setup objectives and targets.
- Category Strategies – Define the optimal strategies.
- Category Tactics – Define the action plan to implement.
- Plan Implementation – Roll out and implement the action plan.
❓What is Category Management Process used for
Help to Identify the Category Role
To define the objectives that the categories should offer to the customers. Each role also affects how to manage the category. Usually, there are 4 Category Roles for each category.
- Routine: Category that is delivering consistent competitive value product.
- Destination: Category that delivers consistent, superior products (Shopping destination – Category of choice)
- Occasional/Seasonal.
- Convenience: Category that delivers good consumer value that customers can’t find elsewhere (One-stop-shopping)
Product Range Review
Having an effective range review process is an opportunity for both Retailers and Manufacturers to positively develop their working relationship and grow their category so both parties can benefit from the improvement of the Shopper’s experience.
Examples of areas to review the Product Range:
- Number of SKUs by status (Active/Inactive/On hold from Purchase or Selling)
- Share of Assortment
- Number of Brands
- Number of Items in Pareto tail
- Brand Efficiency
- Range Efficiency
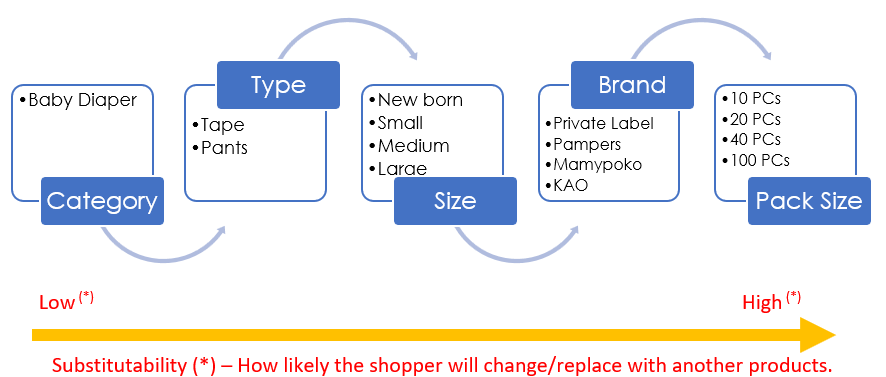
Adapt the product range based on the Customer Decision Tree
Having a clear understanding of the Customer Decision Tree will help retailers or manufacturers to understand the buying habits and decision-making process of the shoppers shopping in the Category.
Example of Customer Decision-Making Process
Suppliers Performance Assessment
They help Retailers to assess their Suppliers in their ability to:
- Generate Volume (Products and Availability)
- Generate Margin
- Lead Innovation (New products)
- Active the category (Promotion)
- Drive Traffic (Shoppers’ engagement)
Setup Category Strategy
A category strategy defines what a category needs to do to perform optimally. For example, to drive traffic, generate cashflow or margin, Reinforce customer retention, etc....
Setup Category Tactics
Set and combinations of actions to take on Range, Space, Price, and Promotion to drive category growth.
For Example,
|
Goal |
Grow Sales /
Maintain Margin |
Decrease
Sales/Increase Profit |
|
Range |
- Create high-quality
Private Label |
- Reduce the number
of EDLP (Everyday Low Price) - Reduce product
range by avoiding redundancy |
|
Space |
- Place more
profitable items in leading positions |
- Place Private Labels
in leading positions |
|
Pricing |
- To match price
point with competitors but not lead |
- Raise price point
whenever possible |
|
Promotions |
- Try to match with
the competitors, especially during the period when they are aggressively
doing a promotion |
- Reduce promotion
frequency |
How is data collected and analyzed during the Category Management Process?
Data collection and analysis in the Category Management Process are crucial steps that involve various methods and tools to ensure informed decision-making. Typically, retailers and manufacturers utilize a combination of sales data, customer feedback, market research, and analytics software to gather relevant information about product performance, consumer preferences, and market trends. Advanced data analytics tools and software solutions are often employed to process and analyze this data, providing valuable insights into category performance, sales trends, and consumer behavior. These insights then inform the strategies and tactics developed during the Category Management Process, enabling retailers and manufacturers to optimize product assortments, pricing strategies, promotional activities, and overall category performance.
What are the key performance indicators (KPIs) commonly used to measure Category performance?
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are essential metrics that retailers and manufacturers use to evaluate and measure category performance effectively. Some commonly used KPIs include sales growth, profit margins, market share, customer satisfaction, inventory turnover, and return on investment (ROI). These KPIs provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of category strategies and tactics, helping stakeholders identify areas for improvement and opportunities for growth. By regularly monitoring and analyzing these KPIs, retailers and manufacturers can make data-driven decisions to optimize category performance, enhance customer experience, and achieve their financial objectives.
How do Retailers and Manufacturers collaborate effectively during the Category Management Process?
Effective collaboration between retailers and manufacturers is essential for the success of the Category Management Process. To foster a productive working relationship, stakeholders often engage in regular communication, joint planning sessions, and collaborative strategy development. Open and transparent communication channels are established to facilitate the sharing of insights, data, and feedback between parties. Additionally, collaborative tools and platforms may be utilized to streamline workflow, coordinate activities, and align goals and objectives. By working together closely and leveraging each other's strengths and expertise, retailers and manufacturers can develop and implement strategies that drive category growth, enhance shopper experience, and create mutual value.
• Category
• Category Role
• Category Strategy
• Category Tactics
• Range Review Process