🎓 Definition
Price index refers to the metric that illustrates how a product, a group of products, categories, or a brand is positioned in the market.
A Retailer uses the Price Index mainly to compare itself with its competitors and adjust its pricing to support its Category Role and Strategies.
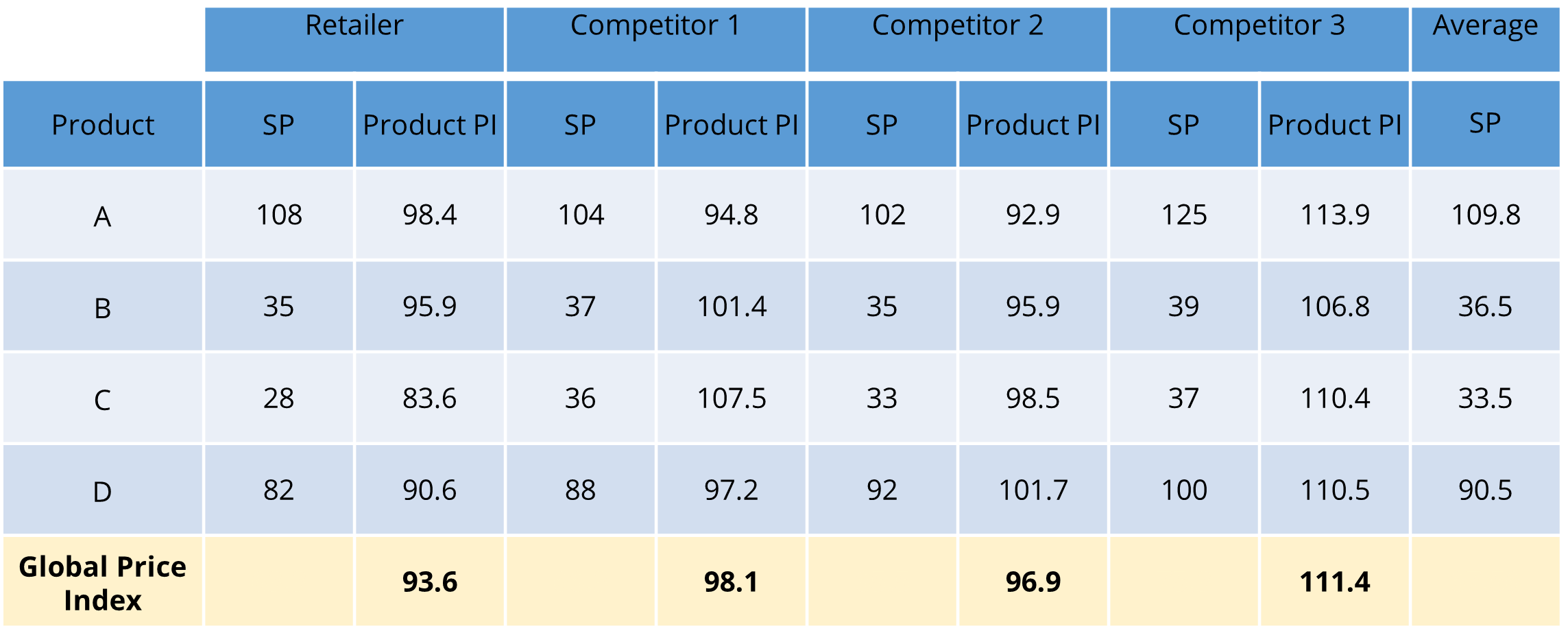
🧪 Example of Price Index Calculation
Price Index Formula= (Product Selling Price/Average Product Selling Price Surveyed) x 100
If the Price Index is 100, then the Selling Price is exactly as the average competitor's Selling Price in the Category. Anything higher than 100 means the Selling Price set is more expensive than the competition. It works the same the other way, anything lower than 100 means that the product is competitively priced. A price index of 97 would mean that the product(s) is/are 3% cheaper compared to the average.
❓What is Price Index used for
- To help the Retailer to understand its price positioning and compare it to its key competitors.
- To measure if its Price Index is aligned with the Pricing Policy and adjust its Price Index accordingly.
- To help Retailer to keep track of price trends within their category(ies). Sudden movements in pricing, up and down, within the category, will have a clear impact on Price Index.
- Price Index also allows measuring the Price fluctuation over different time periods, especially in a Category where Purchase Price are dependent from seasonality, availability, and quality such as Fresh Products.
🎁 Take Aways
Price Index is strongly related to Price Image, it is a metric to drive and support Retailer's Price Image based on Retailer's Price Policy. Not to forget it is one of the key elements to drive customer's perception if a Retailer offers them "value for money"
🧰 Related Working Processes
● Price Image survey
● Customer Panels
● Price Survey (including web scrapping)
How frequently should a retailer update or recalculate their Price Index to ensure it remains accurate and relevant?
Retailers should ideally update or recalculate their Price Index regularly, depending on the volatility and dynamics of their market. While there's no one-size-fits-all answer, it's recommended to review and adjust the Price Index at least quarterly. This frequency allows retailers to stay updated with market fluctuations, competitor pricing changes, and shifts in consumer behavior. By doing so, they can ensure that their pricing strategies remain competitive and aligned with their pricing policies.
Are there any potential drawbacks or limitations to relying solely on the Price Index as a metric for pricing strategy and market positioning?
While the Price Index is a valuable metric for understanding market positioning and competitiveness, relying solely on it can have limitations. The Price Index focuses primarily on comparing selling prices with competitors' averages and may not take into account other crucial factors like product quality, brand perception, or customer preferences. Therefore, using the Price Index alone might lead to overlooking these essential elements, potentially impacting the overall value proposition and customer experience. It's advisable for retailers to complement the Price Index with other metrics and insights to develop a more comprehensive and effective pricing strategy.
How do external factors, such as economic conditions or changes in consumer behavior, impact the Price Index and how should a retailer adjust their strategies accordingly?
External factors like economic conditions, consumer behavior shifts, and market trends can significantly impact the Price Index. For instance, during economic downturns, consumers may become more price-sensitive, leading to increased competition and downward pressure on prices. Similarly, changes in consumer preferences or emerging market trends can influence the perceived value of products, affecting the Price Index. To adjust their strategies accordingly, retailers should continuously monitor these external factors and adapt their pricing policies and promotional activities. This proactive approach allows retailers to maintain a competitive edge, cater to evolving consumer needs, and ensure their Price Index accurately reflects the market dynamics.